navis
Object Separation (VITON-HD) 본문
1. 목차
- 환경설정
- 모델 : VITON-HD
- 코드변경
- 기존 test.py 수정
- 추론 결과
- 결과 확인
- 최종 결과
2. 환경 설정
- AI 모델 테스트 환경
- Ubuntu 22.04(워크스테이션)
- Anaconda
- VS Code
- Python 3.8.18
- 환경설정
git clone <https://github.com/shadow2496/VITON-HD.git>
conda install pytorch==1.6.0 cudatoolkit=9.2 -c pytorch
pip install torchvision
pip install opencv-python torchgeometry
pip install fastapi uvicorn aiofiles && conda install -c conda-forge ffmpeg
3. VITON-HD
https://github.com/shadow2496/VITON-HD
1. 모델 (VITON-HD)
Abstract: The task of image-based virtual try-on aims to transfer a target clothing item onto the corresponding region of a person, which is commonly tackled by fitting the item to the desired body part and fusing the warped item with the person. While an increasing number of studies have been conducted, the resolution of synthesized images is still limited to low (e.g., 256x192), which acts as the critical limitation against satisfying online consumers. We argue that the limitation stems from several challenges: as the resolution increases, the artifacts in the misaligned areas between the warped clothes and the desired clothing regions become noticeable in the final results; the architectures used in existing methods have low performance in generating high-quality body parts and maintaining the texture sharpness of the clothes. To address the challenges, we propose a novel virtual try-on method called VITON-HD that successfully synthesizes 1024x768 virtual try-on images. Specifically, we first prepare the segmentation map to guide our virtual try-on synthesis, and then roughly fit the target clothing item to a given person's body. Next, we propose ALIgnment-Aware Segment (ALIAS) normalization and ALIAS generator to handle the misaligned areas and preserve the details of 1024x768 inputs. Through rigorous comparison with existing methods, we demonstrate that VITON-HD highly surpasses the baselines in terms of synthesized image quality both qualitatively and quantitatively.

4. 코드 변경
test.py
import argparse
import os
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torchgeometry as tgm
from datasets import VITONDataset, VITONDataLoader
from networks import SegGenerator, GMM, ALIASGenerator
from utils import gen_noise, load_checkpoint, save_images
def get_opt():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--name', type=str, required=True)
parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch_size', type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument('--load_height', type=int, default=1024)
parser.add_argument('--load_width', type=int, default=768)
parser.add_argument('--shuffle', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--dataset_dir', type=str, default='./datasets/')
parser.add_argument('--dataset_mode', type=str, default='test')
parser.add_argument('--dataset_list', type=str, default='test_pairs.txt')
parser.add_argument('--checkpoint_dir', type=str, default='./checkpoints/')
parser.add_argument('--save_dir', type=str, default='./results/')
parser.add_argument('--display_freq', type=int, default=1)
parser.add_argument('--seg_checkpoint', type=str, default='seg_final.pth')
parser.add_argument('--gmm_checkpoint', type=str, default='gmm_final.pth')
parser.add_argument('--alias_checkpoint', type=str, default='alias_final.pth')
# common
parser.add_argument('--semantic_nc', type=int, default=13, help='# of human-parsing map classes')
parser.add_argument('--init_type', choices=['normal', 'xavier', 'xavier_uniform', 'kaiming', 'orthogonal', 'none'], default='xavier')
parser.add_argument('--init_variance', type=float, default=0.02, help='variance of the initialization distribution')
# for GMM
parser.add_argument('--grid_size', type=int, default=5)
# for ALIASGenerator
parser.add_argument('--norm_G', type=str, default='spectralaliasinstance')
parser.add_argument('--ngf', type=int, default=64, help='# of generator filters in the first conv layer')
parser.add_argument('--num_upsampling_layers', choices=['normal', 'more', 'most'], default='most',
help='If \'more\', add upsampling layer between the two middle resnet blocks. '
'If \'most\', also add one more (upsampling + resnet) layer at the end of the generator.')
opt = parser.parse_args()
return opt
def test(opt, seg, gmm, alias):
up = nn.Upsample(size=(opt.load_height, opt.load_width), mode='bilinear')
gauss = tgm.image.GaussianBlur((15, 15), (3, 3))
gauss.cuda()
test_dataset = VITONDataset(opt)
test_loader = VITONDataLoader(opt, test_dataset)
with torch.no_grad():
for i, inputs in enumerate(test_loader.data_loader):
img_names = inputs['img_name']
c_names = inputs['c_name']['unpaired']
img_agnostic = inputs['img_agnostic'].cuda()
parse_agnostic = inputs['parse_agnostic'].cuda()
pose = inputs['pose'].cuda()
c = inputs['cloth']['unpaired'].cuda()
cm = inputs['cloth_mask']['unpaired'].cuda()
# Part 1. Segmentation generation
parse_agnostic_down = F.interpolate(parse_agnostic, size=(256, 192), mode='bilinear')
pose_down = F.interpolate(pose, size=(256, 192), mode='bilinear')
c_masked_down = F.interpolate(c * cm, size=(256, 192), mode='bilinear')
cm_down = F.interpolate(cm, size=(256, 192), mode='bilinear')
seg_input = torch.cat((cm_down, c_masked_down, parse_agnostic_down, pose_down, gen_noise(cm_down.size()).cuda()), dim=1)
parse_pred_down = seg(seg_input)
parse_pred = gauss(up(parse_pred_down))
parse_pred = parse_pred.argmax(dim=1)[:, None]
parse_old = torch.zeros(parse_pred.size(0), 13, opt.load_height, opt.load_width, dtype=torch.float).cuda()
parse_old.scatter_(1, parse_pred, 1.0)
labels = {
0: ['background', [0]],
1: ['paste', [2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]],
2: ['upper', [3]],
3: ['hair', [1]],
4: ['left_arm', [5]],
5: ['right_arm', [6]],
6: ['noise', [12]]
}
parse = torch.zeros(parse_pred.size(0), 7, opt.load_height, opt.load_width, dtype=torch.float).cuda()
for j in range(len(labels)):
for label in labels[j][1]:
parse[:, j] += parse_old[:, label]
# Part 2. Clothes Deformation
agnostic_gmm = F.interpolate(img_agnostic, size=(256, 192), mode='nearest')
parse_cloth_gmm = F.interpolate(parse[:, 2:3], size=(256, 192), mode='nearest')
pose_gmm = F.interpolate(pose, size=(256, 192), mode='nearest')
c_gmm = F.interpolate(c, size=(256, 192), mode='nearest')
gmm_input = torch.cat((parse_cloth_gmm, pose_gmm, agnostic_gmm), dim=1)
_, warped_grid = gmm(gmm_input, c_gmm)
warped_c = F.grid_sample(c, warped_grid, padding_mode='border')
warped_cm = F.grid_sample(cm, warped_grid, padding_mode='border')
# Part 3. Try-on synthesis
misalign_mask = parse[:, 2:3] - warped_cm
misalign_mask[misalign_mask < 0.0] = 0.0
parse_div = torch.cat((parse, misalign_mask), dim=1)
parse_div[:, 2:3] -= misalign_mask
output = alias(torch.cat((img_agnostic, pose, warped_c), dim=1), parse, parse_div, misalign_mask)
unpaired_names = []
for img_name, c_name in zip(img_names, c_names):
unpaired_names.append('{}_{}'.format(img_name.split('_')[0], c_name))
save_images(output, unpaired_names, os.path.join(opt.save_dir, opt.name))
if (i + 1) % opt.display_freq == 0:
print("step: {}".format(i + 1))
def main():
opt = get_opt()
print(opt)
if not os.path.exists(os.path.join(opt.save_dir, opt.name)):
os.makedirs(os.path.join(opt.save_dir, opt.name))
seg = SegGenerator(opt, input_nc=opt.semantic_nc + 8, output_nc=opt.semantic_nc)
gmm = GMM(opt, inputA_nc=7, inputB_nc=3)
opt.semantic_nc = 7
alias = ALIASGenerator(opt, input_nc=9)
opt.semantic_nc = 13
load_checkpoint(seg, os.path.join(opt.checkpoint_dir, opt.seg_checkpoint))
load_checkpoint(gmm, os.path.join(opt.checkpoint_dir, opt.gmm_checkpoint))
load_checkpoint(alias, os.path.join(opt.checkpoint_dir, opt.alias_checkpoint))
seg.cuda().eval()
gmm.cuda().eval()
alias.cuda().eval()
test(opt, seg, gmm, alias)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()input Video Frame (VITON-HD)
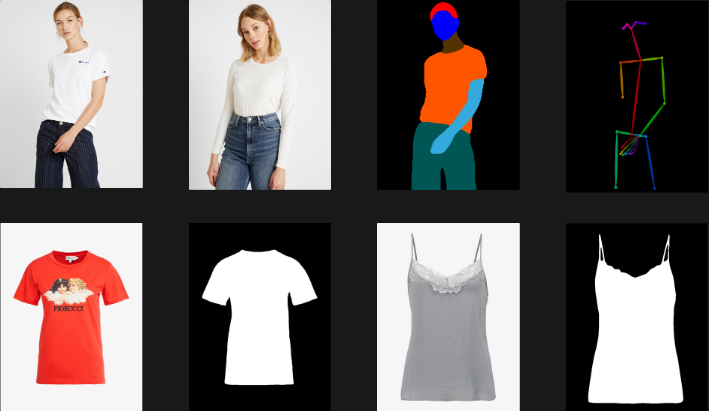
이것은 제공된 데이터로 추론한 결과입니다. 데이터셋을 학습할 때는 인물 마스크, 포즈를 포함하여 학습 해야 하며, 의류에 대해서도 마스크 이미지와 함께 학습해야 합니다.
output Video Frame (VITON-HD)
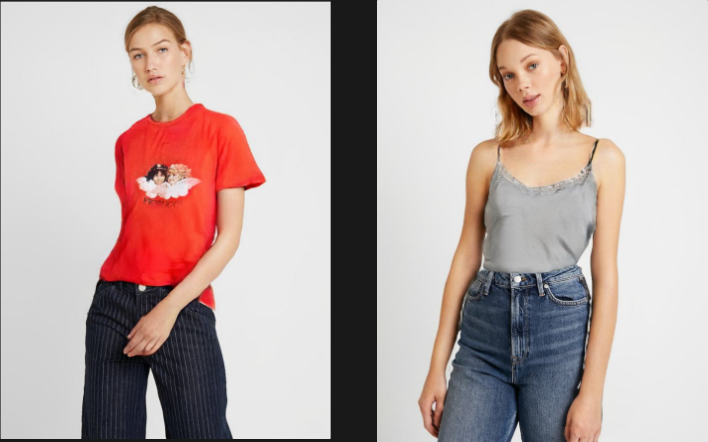

의류 영역이 자세에 따라 변하며 적용됩니다.
프레임에 지정된 의류를 적용함으로써 비디오의 일관성이 유지될 것으로 예상됩니다.
6. 최종 결과

모델에서 제공하는 학습 자료를 보면, 추가적인 인페인팅과 마스크 작업이 필요할 것으로 보입니다. 그러나 학습에 대한 세부 사항은 더 자세히 파악해야 할 것 같습니다.

json 파일로 제공되는 포즈 키포인트 부분도 이해하기 어렵습니다. 아마 이 정보를 통해 결과를 도출하는 것으로 보이지만 알 수 없습니다.
'AI' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Video Upscaling (ResShift) (0) | 2024.06.16 |
|---|---|
| Video Upscaling (StableSR) (0) | 2024.06.16 |
| 우분투 Anaconda Navigator 설치 및 실행 (0) | 2024.05.23 |
| Video Upscaling (CodeFormer) (0) | 2024.05.22 |
| Object Separation (cloth-segmentation) (0) | 2024.05.22 |



